menu


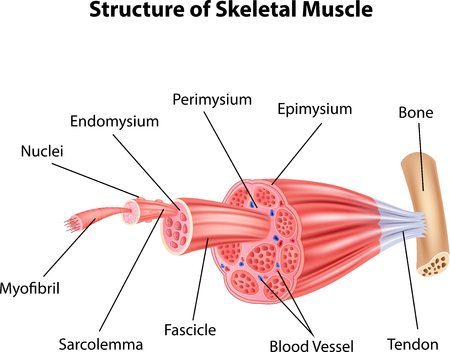
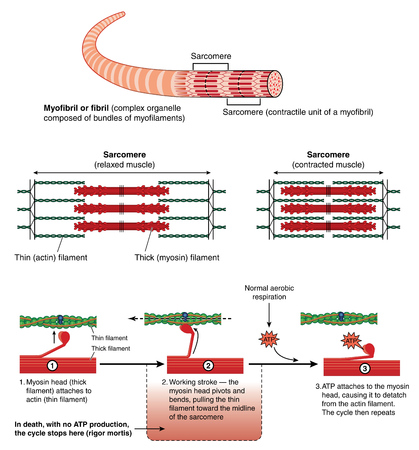
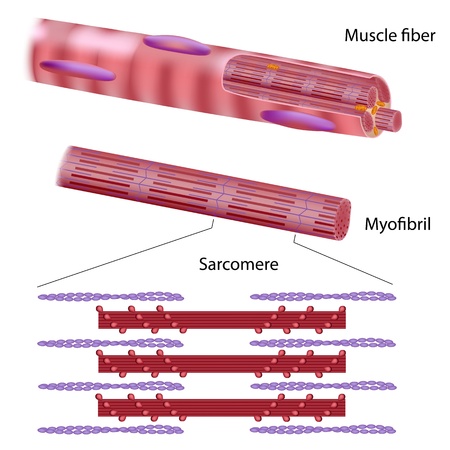
Skeletal muscles are made out of many bundles of muscle fiber, which are basically giant cells not much thinner than human hair and as long as 12 inches. Within the muscle fiber itself are thousands of tiny individual units for contracting called sarcomeres. These sarcomeres are lined up end to end in cylinders called myofibrils. Within each muscle fiber are many microfibrils. now hold on this is where it starts to get complicated, the enplane boundaries of the sarcomere are called Z lines.Centered between these two lines but not touching are filaments of a protein called myosin. But attached to the Lines are protein filaments called actin. The actin and myosin interaction is what causes the actual muscular contraction. Now surrounding the myofibrils which contain all the sarcomeres is a reservoir for holding calcium ions, which is necessary for contraction called a sarcoplasmic rectilium. This entire package is encased by a membrane called a sarcolema, which contains receptor sites for nerve stimulation.
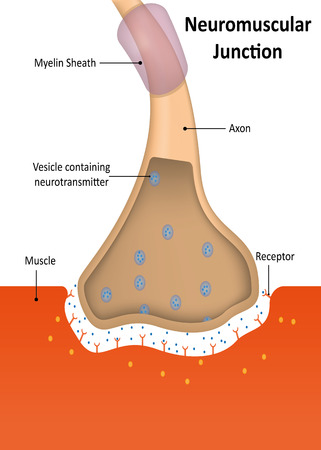
Nerve impulse
In order for a muscle to contract it has to be stimulated by nerve impulse. One nerve cell or motor unit can stimulate as little as a few or as many as hundreds of muscle cells. This one cell plus all the muscle cell it stimulates is called a motor unit.
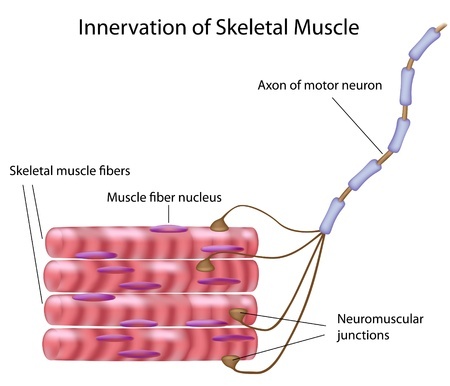
The chemical message, a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, binds to receptors on the outside of the muscle fiber. That starts a chemical reaction within the muscle. The proteins inside muscle fibers are organized into long chains that can interact with each other, reorganizing to shorten and relax. When acetylcholine reaches receptors on the membranes of muscle fibers, membrane channels open up and the process that contracts a relaxed muscle fibers begins:
Open channels allow an influx of sodium ions into the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber.
The sodium influx also sends a message within the muscle fiber to trigger the release of stored calcium ions.
The calcium ions diffuse into the muscle fiber.
The relationship between the chains of proteins within the muscle cells changes, leading to the contraction.
Open channels allow an influx of sodium ions into the cytoplasm of the muscle fiber.
The sodium influx also sends a message within the muscle fiber to trigger the release of stored calcium ions.
The calcium ions diffuse into the muscle fiber.
The relationship between the chains of proteins within the muscle cells changes, leading to the contraction.
When the stimulation of the motor neuron providing the impulse to the muscle fibers stops, the chemical reaction that causes the rearrangement of the muscle fibers' proteins is stopped. This reverses the chemical processes in the muscle fibers and the muscle relaxes.
About Us
Training people for over 30 years, Body Plus has the experience and credentials to deliver results to anyone willing to work hard and eat right! Don’t waste precious time. It’s time to get fit NOW!!!